What Network Management Requirement Should Be Addressed Before The Service Is Acquired
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to accept advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Virtual network design considerations and configuration options for Azure Active Directory Domain Services
Azure Active Directory Domain Services (Azure Advertising DS) provides authentication and direction services to other applications and workloads. Network connectivity is a key component. Without correctly configured virtual network resources, applications and workloads can't communicate with and use the features provided by Azure AD DS. Plan your virtual network requirements to brand sure that Azure AD DS tin serve your applications and workloads every bit needed.
This article outlines pattern considerations and requirements for an Azure virtual network to support Azure Advertisement DS.
Azure virtual network blueprint
To provide network connectivity and allow applications and services to authenticate against an Azure Advertising DS managed domain, you use an Azure virtual network and subnet. Ideally, the managed domain should be deployed into its own virtual network.
You tin include a dissever application subnet in the same virtual network to host your direction VM or light application workloads. A separate virtual network for larger or complex application workloads, peered to the Azure Advert DS virtual network, is usually the almost advisable blueprint.
Other designs choices are valid, provided you encounter the requirements outlined in the following sections for the virtual network and subnet.
As you design the virtual network for Azure AD DS, the following considerations utilise:
- Azure AD DS must be deployed into the same Azure region as your virtual network.
- At this time, y'all tin can just deploy 1 managed domain per Azure Advertizement tenant. The managed domain is deployed to single region. Make sure that y'all create or select a virtual network in a region that supports Azure AD DS.
- Consider the proximity of other Azure regions and the virtual networks that host your application workloads.
- To minimize latency, keep your core applications close to, or in the same region as, the virtual network subnet for your managed domain. You can use virtual network peering or virtual private network (VPN) connections betwixt Azure virtual networks. These connectedness options are discussed in a following section.
- The virtual network can't rely on DNS services other than those services provided by the managed domain.
- Azure AD DS provides its own DNS service. The virtual network must be configured to apply these DNS service addresses. Name resolution for additional namespaces tin be accomplished using conditional forwarders.
- You can't utilize custom DNS server settings to straight queries from other DNS servers, including on VMs. Resources in the virtual network must use the DNS service provided by the managed domain.
Important
Y'all can't move Azure Ad DS to a different virtual network after yous've enabled the service.
A managed domain connects to a subnet in an Azure virtual network. Pattern this subnet for Azure AD DS with the following considerations:
- A managed domain must be deployed in its own subnet. Don't employ an existing subnet or a gateway subnet. This includes the usage of remote gateways settings in the virtual network peering which puts the managed domain in an unsupported state.
- A network security group is created during the deployment of a managed domain. This network security group contains the required rules for right service communication.
- Don't create or use an existing network security group with your own custom rules.
- A managed domain requires 3-v IP addresses. Make sure that your subnet IP address range can provide this number of addresses.
- Restricting the available IP addresses can prevent the managed domain from maintaining two domain controllers.
The following example diagram outlines a valid design where the managed domain has its own subnet, in that location's a gateway subnet for external connectivity, and application workloads are in a connected subnet within the virtual network:
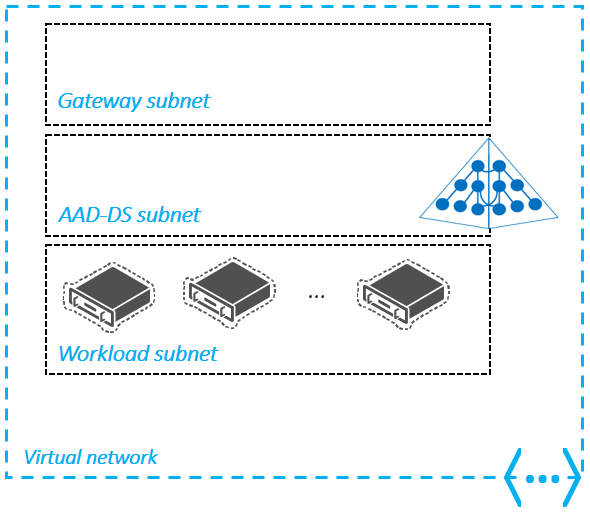
Every bit noted in the previous section, you can only create a managed domain in a single virtual network in Azure, and only one managed domain can exist created per Azure Advertisement tenant. Based on this architecture, you may need to connect 1 or more than virtual networks that host your application workloads to your managed domain'south virtual network.
You lot can connect awarding workloads hosted in other Azure virtual networks using one of the following methods:
- Virtual network peering
- Virtual private networking (VPN)
Virtual network peering
Virtual network peering is a mechanism that connects two virtual networks in the same region through the Azure courage network. Global virtual network peering can connect virtual network across Azure regions. Once peered, the 2 virtual networks permit resource, such every bit VMs, communicate with each other straight using private IP addresses. Using virtual network peering lets y'all deploy a managed domain with your application workloads deployed in other virtual networks.
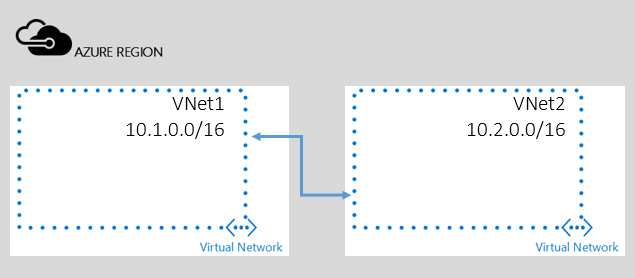
For more information, encounter Azure virtual network peering overview.
Virtual Private Networking (VPN)
You lot can connect a virtual network to another virtual network (VNet-to-VNet) in the same fashion that y'all tin configure a virtual network to an on-bounds site location. Both connections use a VPN gateway to create a secure tunnel using IPsec/IKE. This connexion model lets you lot deploy the managed domain into an Azure virtual network and so connect on-premises locations or other clouds.
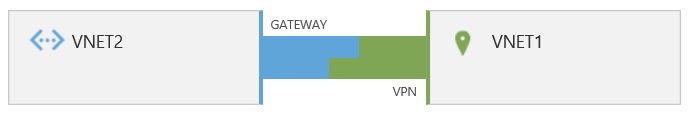
For more than information on using virtual private networking, read Configure a VNet-to-VNet VPN gateway connexion by using the Azure portal.
Proper noun resolution when connecting virtual networks
Virtual networks connected to the managed domain's virtual network typically have their own DNS settings. When you lot connect virtual networks, it doesn't automatically configure name resolution for the connecting virtual network to resolve services provided by the managed domain. Name resolution on the connecting virtual networks must be configured to enable application workloads to locate the managed domain.
You can enable name resolution using conditional DNS forwarders on the DNS server supporting the connecting virtual networks, or by using the same DNS IP addresses from the managed domain's virtual network.
A managed domain creates some networking resources during deployment. These resources are needed for successful operation and management of the managed domain, and shouldn't be manually configured.
Don't lock the networking resources used by Azure Advertizing DS. If networking resources get locked, they tin't be deleted. When domain controllers demand to exist rebuilt in that case, new networking resources with different IP addresses need to be created.
| Azure resources | Description |
|---|---|
| Network interface carte | Azure AD DS hosts the managed domain on two domain controllers (DCs) that run on Windows Server as Azure VMs. Each VM has a virtual network interface that connects to your virtual network subnet. |
| Dynamic standard public IP address | Azure Advertising DS communicates with the synchronization and management service using a Standard SKU public IP address. For more information about public IP addresses, see IP accost types and allocation methods in Azure. |
| Azure standard load balancer | Azure AD DS uses a Standard SKU load balancer for network accost translation (NAT) and load balancing (when used with secure LDAP). For more than information nigh Azure load balancers, see What is Azure Load Balancer? |
| Network address translation (NAT) rules | Azure Advertisement DS creates and uses two Inbound NAT rules on the load balancer for secure PowerShell remoting. If a Standard SKU load balancer is used, it will have an Outbound NAT Dominion too. For the Bones SKU load balancer, no Outbound NAT rule is required. |
| Load balancer rules | When a managed domain is configured for secure LDAP on TCP port 636, iii rules are created and used on a load balancer to distribute the traffic. |
Warning
Don't delete or change any of the network resources created by Azure Advertizing DS, such as manually configuring the load balancer or rules. If yous delete or change whatsoever of the network resource, an Azure Advertising DS service outage may occur.
Network security groups and required ports
A network security group (NSG) contains a list of rules that allow or deny network traffic in an Azure virtual network. When you deploy a managed domain, a network security group is created with a set of rules that permit the service provide authentication and direction functions. This default network security group is associated with the virtual network subnet your managed domain is deployed into.
The following sections cover network security groups and Inbound and Outbound port requirements.
Entering connectivity
The following network security grouping Inbound rules are required for the managed domain to provide authentication and management services. Don't edit or delete these network security group rules for the virtual network subnet your managed domain is deployed into.
| Inbound port number | Protocol | Source | Destination | Activeness | Required | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5986 | TCP | AzureActiveDirectoryDomainServices | Any | Allow | Aye | Management of your domain. |
| 3389 | TCP | CorpNetSaw | Any | Let | Optional | Debugging for support. |
An Azure standard load balancer is created that requires these rules to be place. This network security group secures Azure Advertising DS and is required for the managed domain to work correctly. Don't delete this network security grouping. The load balancer won't work correctly without it.
If needed, y'all can create the required network security grouping and rules using Azure PowerShell.
Warning
When you lot associate a misconfigured network security grouping or a user defined route table with the subnet in which the managed domain is deployed, you may disrupt Microsoft's ability to service and manage the domain. Synchronization between your Azure AD tenant and your managed domain is also disrupted. Follow all listed requirements to avoid an unsupported configuration that could interruption sync, patching, or management.
If you use secure LDAP, you can add the required TCP port 636 rule to permit external traffic if needed. Adding this rule doesn't place your network security group rules in an unsupported state. For more data, encounter Lock down secure LDAP access over the cyberspace
The Azure SLA doesn't use to deployments that are blocked from updates or management by an improperly configured network security group or user defined route table. A broken network configuration tin can also prevent security patches from being applied.
Outbound connectivity
For Outbound connectivity, you can either keep AllowVnetOutbound and AllowInternetOutBound or restrict Outbound traffic past using ServiceTags listed in the following tabular array. The ServiceTag for AzureUpdateDelivery must be added via PowerShell.
Filtered Outbound traffic is not supported on Classic deployments.
| Outbound port number | Protocol | Source | Destination | Activeness | Required | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 443 | TCP | Whatsoever | AzureActiveDirectoryDomainServices | Allow | Yes | Advice with the Azure AD Domain Services management service. |
| 443 | TCP | Any | AzureMonitor | Allow | Yep | Monitoring of the virtual machines. |
| 443 | TCP | Whatsoever | Storage | Allow | Yeah | Advice with Azure Storage. |
| 443 | TCP | Any | AzureActiveDirectory | Allow | Aye | Communication with Azure Active Directory. |
| 443 | TCP | Any | AzureUpdateDelivery | Permit | Aye | Advice with Windows Update. |
| 80 | TCP | Whatsoever | AzureFrontDoor.FirstParty | Let | Yes | Download of patches from Windows Update. |
| 443 | TCP | Whatever | GuestAndHybridManagement | Allow | Yeah | Automated management of security patches. |
Port 5986 - management using PowerShell remoting
-
Used to perform direction tasks using PowerShell remoting in your managed domain.
-
Without admission to this port, your managed domain tin can't be updated, configured, backed-upward, or monitored.
-
For managed domains that use a Resources Manager-based virtual network, you tin restrict inbound admission to this port to the AzureActiveDirectoryDomainServices service tag.
- For legacy managed domains using a Archetype-based virtual network, you can restrict inbound access to this port to the following source IP addresses: 52.180.183.8, 23.101.0.70, 52.225.184.198, 52.179.126.223, 13.74.249.156, 52.187.117.83, 52.161.13.95, 104.twoscore.156.18, and 104.40.87.209.
Note
In 2017, Azure AD Domain Services became available to host in an Azure Resources Manager network. Since and so, nosotros have been able to build a more than secure service using the Azure Resource Director's modern capabilities. Because Azure Resources Manager deployments fully supersede classic deployments, Azure AD DS classic virtual network deployments will exist retired on March i, 2023.
For more information, see the official deprecation notice
Port 3389 - management using remote desktop
- Used for remote desktop connections to domain controllers in your managed domain.
- The default network security group rule uses the CorpNetSaw service tag to further restrict traffic.
- This service tag permits only secure access workstations on the Microsoft corporate network to employ remote desktop to the managed domain.
- Admission is only allowed with business justification, such as for management or troubleshooting scenarios.
- This rule tin can be ready to Deny, and just set up to Permit when required. Most management and monitoring tasks are performed using PowerShell remoting. RDP is merely used in the rare event that Microsoft needs to connect remotely to your managed domain for advanced troubleshooting.
You can't manually select the CorpNetSaw service tag from the portal if yous try to edit this network security group rule. You must use Azure PowerShell or the Azure CLI to manually configure a rule that uses the CorpNetSaw service tag.
For example, you tin use the following script to create a rule assuasive RDP:
Become-AzNetworkSecurityGroup -Proper noun "nsg-proper name" -ResourceGroupName "resource-group-name" | Add-AzNetworkSecurityRuleConfig -Name "new-dominion-name" -Access "Permit" -Protocol "TCP" -Direction "Inbound" -Priority "priority-number" -SourceAddressPrefix "CorpNetSaw" -SourcePortRange "*" -DestinationPortRange "3389" -DestinationAddressPrefix "*" | Set-AzNetworkSecurityGroup User-defined routes
User-defined routes aren't created by default, and aren't needed for Azure AD DS to work correctly. If y'all're required to apply route tables, avert making whatsoever changes to the 0.0.0.0 route. Changes to this road disrupt Azure Advert DS and puts the managed domain in an unsupported state.
You must besides route inbound traffic from the IP addresses included in the respective Azure service tags to the managed domain'south subnet. For more data on service tags and their associated IP address from, come across Azure IP Ranges and Service Tags - Public Cloud.
Circumspection
These Azure datacenter IP ranges tin change without notice. Ensure yous have processes to validate y'all have the latest IP addresses.
Next steps
For more information about some of the network resources and connexion options used by Azure AD DS, meet the following manufactures:
- Azure virtual network peering
- Azure VPN gateways
- Azure network security groups
Feedback
Submit and view feedback for
What Network Management Requirement Should Be Addressed Before The Service Is Acquired,
Source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory-domain-services/network-considerations
Posted by: jonesjusy1993.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Network Management Requirement Should Be Addressed Before The Service Is Acquired"
Post a Comment